Welcome to our blog where we dive into the world of economics and consumer behavior. We explore the difference between marginal and total utility this shows our decision and satisfaction in a world with limited resources.
Define Utility
Satisfaction drawn by the consumer from consuming a certain amount of good is called utility. This blog shows the difference between total utility and marginal utility.
Total Utility
Total satisfaction drawn by the consumer from the consumption of a certain amount of good also represents the cumulative effect of all units consumed and reflects the total level of satisfaction experienced by the consumer hence called the total utility.
For Eg- Suppose a consumer consumes 2 oranges. The first orange gives him 10 utils, the second orange gives him 8 utils the Total utility is equal to 18 utils.
Marginal Utility
Marginal utility refers to the additional satisfaction or usefulness gained from consuming one additional unit of a good or service. It focuses on the change in total utility resulting from consuming an extra unit. Marginal utility helps us understand how the satisfaction derived from each additional unit of a good diminishes as consumption increases.
For Eg- Suppose a consumer consumes 2 oranges. The first orange gives him 10 utils, the second orange gives him 8 utils the Marginal utility is equal to 8 utils.
Difference between Total and Marginal utility
| TOTAL UTILITY | MARGINAL UTILITY | |
| Consumer satisfaction is the overall measure of contentment that individuals experience when using or consuming specific goods and services. | Consumer satisfaction is the level of contentment obtained by a consumer through the incremental consumption of a unit of specific goods or services | |
| As consumption increases, the total utility also increases. | With an increase in total utility, the marginal utility tends to diminish. | |
| With an increase in total utility, the marginal utility tends to diminish. | With the consumption of each additional unit, the marginal utility decreases. |
Law of diminishing marginal utility
This law states that as a consumer consumes more and more units of a commodity, the utility obtained from each additional unit goes on decreasing.
Soon situation comes when marginal utility becomes 0 and total utility becomes maximum
If the consumer consumes more units beyond that level, then MU becomes negative and TU starts falling
Therefore. a rational consumer will not consume beyond 0 MU.
This law can be explained with the help o the following example.
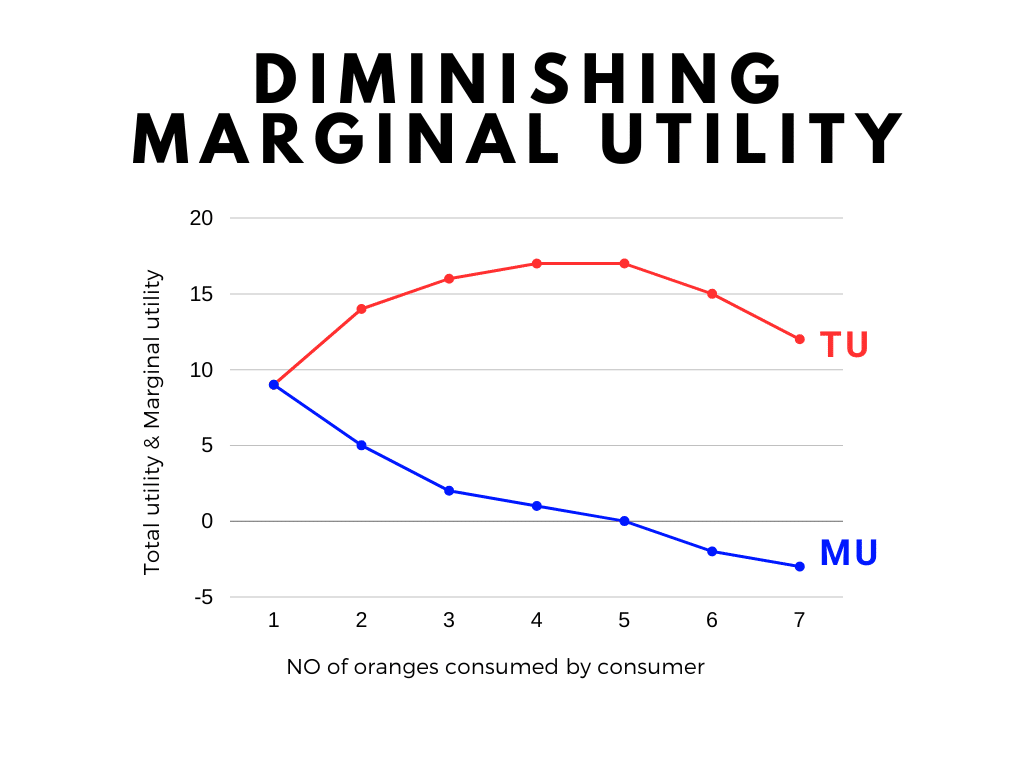
| NO OF ORANGES | TU {UTILS} | MU {UTILS} |
| 1 | 9 | 9 |
| 2 | 14 | 5 |
| 3 | 16 | 2 |
| 4 | 17 | 1 |
| 5 | 17 | 0 |
| 6 | 15 | -2 |
In the above example, the consumer consumes 5 oranges, then he gets maximum utility because then MU is 0 and TU is top. After that MU becomes negative and TU starts falling.
The below graph shows the above example for a better understanding of diminishing marginal utility.
What is the point of satiety?
When marginal utility becomes 0 then it is called the point of satiety because then consumers get maximum utility.
CONCLUSION
Total utility represents overall satisfaction, while marginal utility measures additional satisfaction. Understanding the relationship between TU and MU helps individuals make rational choices to maximize their satisfaction. By recognizing the diminishing returns of marginal utility, individuals can allocate their resources effectively and focus on goods or services that provide the most value. Ultimately, grasping the concepts of TU and MU empowers individuals to make informed decisions that optimize their overall satisfaction.
Comment below and share your thought, if you like the post please share it.
Also Please check out What is the Definition of the Business Cycle and its Phases?



0 Comments